Today's job market requires individuals to have a solid foundation in computer skills. This is not just a competitive advantage but a necessity in nearly every job.
In this article, we'll explore how to effectively list your computer skills on your resume to catch the eye of potential employers.
From basic word processing to advanced programming, you'll find various examples and tips to help you create a standout resume.
Computer skills examples in resumes
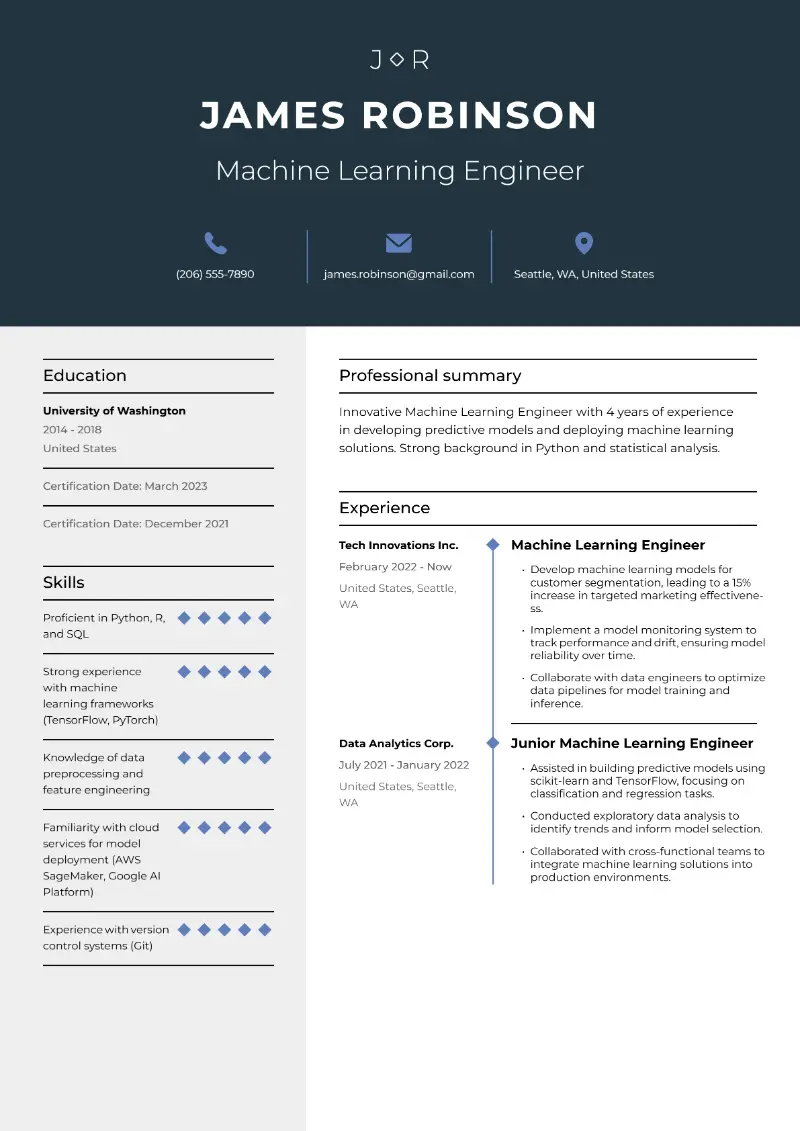
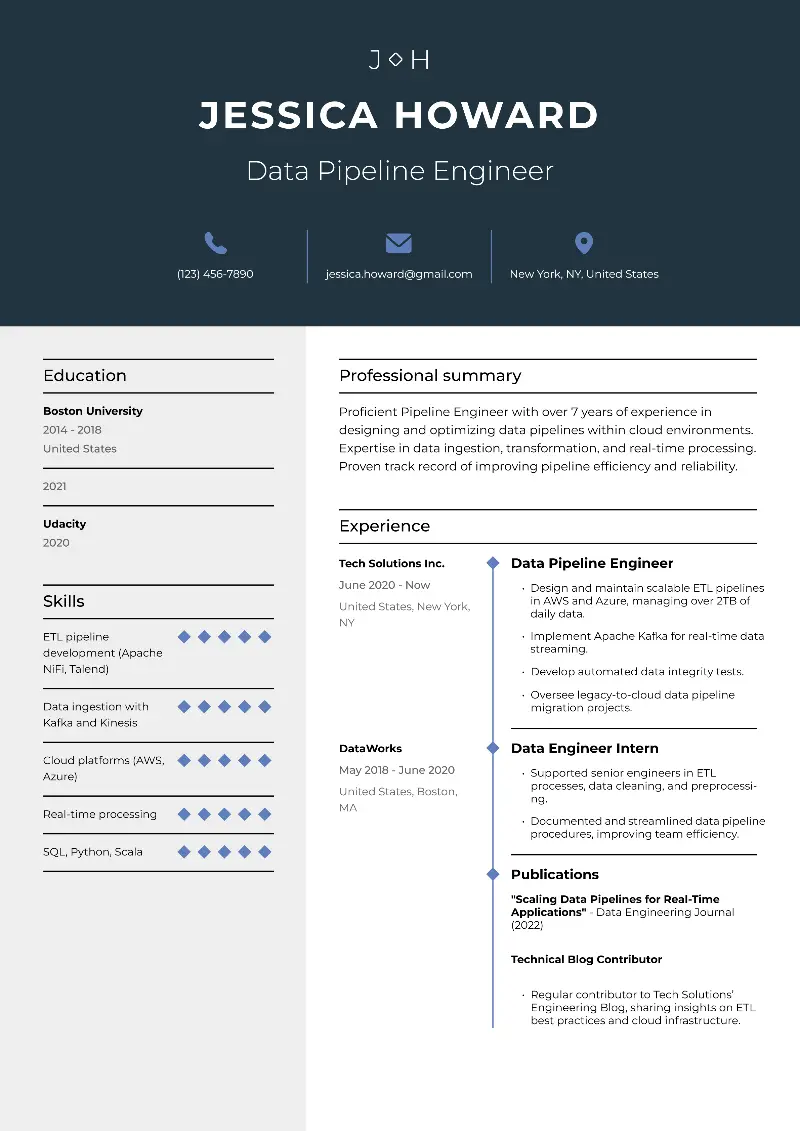
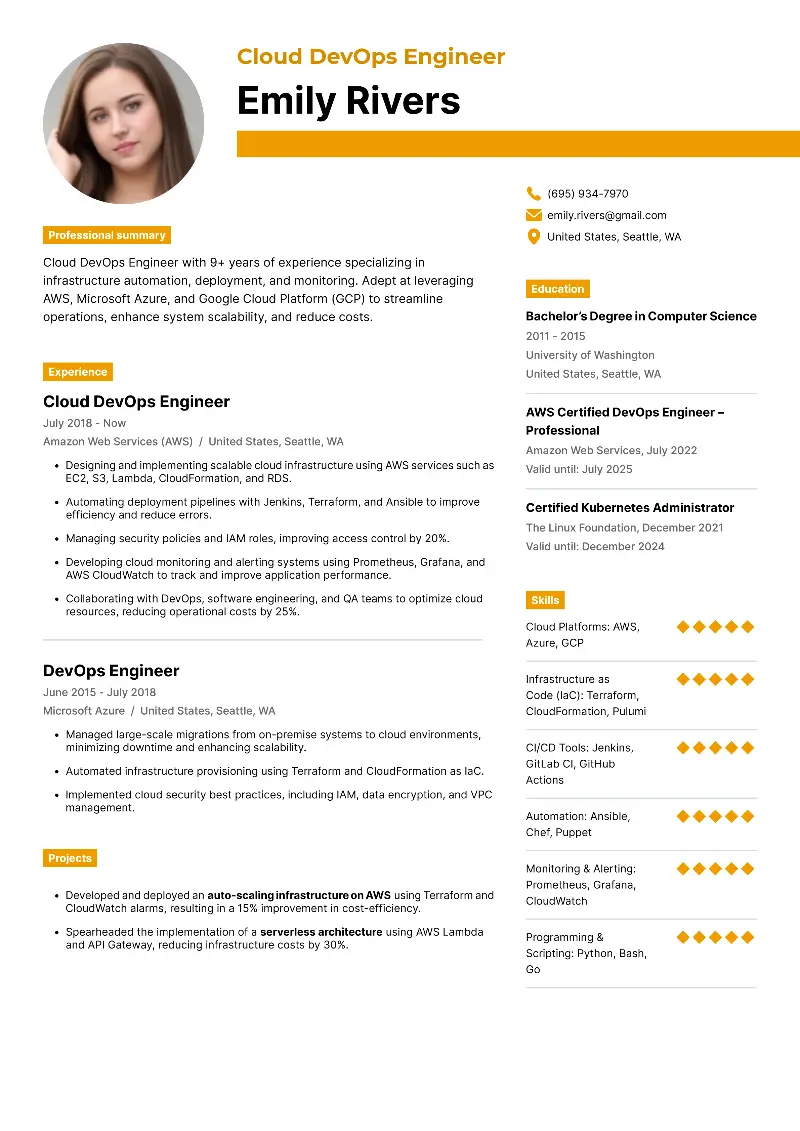
Here are samples of resumes for different jobs that include computer skills:
What are computer skills?
Computer skills refer to the proficiency and knowledge individuals possess in using computers and related technology to perform various tasks effectively.
These competencies encompass a wide range of abilities, from basic tasks such as navigating the internet to more advanced ones like programming, data analysis, and cybersecurity.
It's important to note that computer skills for resume are not just limited to technical abilities. Soft skills like problem-solving, adaptability, and communication are also crucial in using technology effectively.
The capacity to rapidly acquire knowledge of new software and programs is a highly beneficial mastery in today's constantly changing world.
With the increasing reliance on technology in the workplace, demonstrating a high level of computer proficiency can help you stand out.
How to list computer skills on a resume?
When creating your resume, strategically highlighting your hardware and software skills can make you a more attractive candidate to potential employers.
Here are a few essential pointers to bear in mind:
| Tip | Details |
|---|---|
| Create a dedicated section | Having a designated part of your resume solely focused on your computer abilities will make it easier for employers to quickly scan the information. This section can be titled "Computer Skills", "Technical Proficiencies", or a similar designation. |
| Be specific | Rather than stating "proficient in MS Office", indicate which specific programs you possess skills in, such as Excel, Word, or PowerPoint. This will grant employers a clearer perception of your strengths and weaknesses and where you can add value. |
| Use keywords | Look for relevant keywords related to computer proficiency that the employer is seeking in the job description. Incorporate them into your resume, as it will show that you have the necessary skills for the role. |
| Include relevant certifications | If you have any relevant certifications or training in specific computer programs, be certain to add them to your resume. This will demonstrate that you have taken the time to enhance your skills and are committed to staying up-to-date with technology. |
| Highlight your experience | Be sure to demonstrate how you have applied these computer skills in previous roles. This will allow employers to gain insight into your potential impact on their organization. |
| Keep it concise | While it's essential to highlight your computer knowledge, avoid overwhelming the reader with an extensive list. Focus on the most relevant and impactful skills that demonstrate your ability to excel in the role. |
| Mention skill level where appropriate | Indicate whether your capacities are beginner, intermediate, or advanced to give employers a better understanding of your proficiency. |
A computer is like a violin. You can imagine it making beautiful music, but you have to learn how to play it.
Where else can I mention computer skills?
Cover letter
While your cover letter should be primarily focused on expressing your interest in the position and highlighting your qualifications, you can briefly mention your computer skills for resume if they are particularly relevant to the job.
You can provide examples of how your computer knowledge has contributed to your past work experiences or projects, emphasizing their importance in the role you're applying for.
Avoid repeating the exact list from your resume. Instead, use the cover letter to provide context and demonstrate how your technical expertise aligns with the needs of the employer.
Create your professional Cover letter in 10 minutes for FREE
Build My Cover Letter
Interview
During the interview, you may be asked specific interview questions about your computer skills to assess your proficiency and suitability for the role. Be prepared to discuss your experience with the software and technical tools listed on your resume.
If you possess advanced or specialized computer skills relevant to the position, be ready to demonstrate your proficiency through practical exercises or case studies, if requested.
Additionally, use the interview as an opportunity to convey your willingness and ability to learn new technologies and adapt to evolving software trends.
I’m very comfortable with Microsoft Office Suite, especially Excel for data analysis and reporting. I also have experience using Google Workspace, Slack, and basic project management tools like Trello and Asana.
Overall, effectively showcasing your computer skills for resume throughout the job application process can help you demonstrate your readiness to excel in a technology-driven work environment.
Basic computer skills for resume
In the modern era of technology, almost every position necessitates a fundamental understanding of using computers. Basic computer skills for a resume showcase your ability to navigate digital environments effectively, manage information, and communicate efficiently.
| Skill | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Proficient in Microsoft Office suite | Mention your proficiency in using Microsoft Word for text processing, Microsoft Excel for spreadsheets, and Microsoft PowerPoint for presentations. |
| Email and calendar management | Highlight your ability to use email clients such as Microsoft Outlook or Gmail for professional correspondence and scheduling meetings. |
| Internet browsing | Note your familiarity with web browsers like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, or Microsoft Edge for research and online communication. |
| File management | Emphasize your skills in organizing files and folders on a computer system, including tasks such as renaming files, creating directories, and managing file formats. |
| Basic data entry | Mention your ability to accurately input data into software applications or databases using keyboarding skills. |
| Troubleshooting | Highlight your capacity to diagnose and resolve common hardware and software issues that may arise while using a computer. |
| Communication tools | If relevant to the job, include proficiency in collaboration tools such as Slack, Microsoft Teams, or Zoom for remote communication and teamwork. |
| Cybersecurity awareness | Note your understanding of basic cybersecurity principles, such as password security, malware protection, and phishing awareness. |
| Operating system navigation | Demonstrate your comfort working within major operating systems like Windows, macOS, or Linux for everyday tasks and system operations. |
In a nutshell, showcasing computer proficiency on your resume is imperative in today's job climate. It displays your versatility and skill in technology, positioning you as a valuable resource for any business.
Typing and keyboard skills
These are fundamental computer skills for resume that play a critical role in both personal and professional settings.
Key components:
- Typing Speed. The ability to type quickly is essential for many jobs, especially those that require frequent writing, data entry, or communication. A good typing speed generally ranges between 40 to 60 words per minute (WPM) for most professions.
- Accuracy. While speed is important, accuracy is crucial to avoid errors. Typing with minimal mistakes reduces the time spent proofreading and correcting, enhancing overall efficiency.
- Keyboard Shortcuts. Mastering keyboard shortcuts is a valuable skill that allows users to perform actions quickly without relying on a mouse. Shortcuts like Ctrl + C (copy), + V (paste), or Alt + Tab (switch between windows) save time and streamline workflows.
- Touch Typing. This computer skill involves typing without looking at the keyboard, relying on muscle memory to locate keys.
- Ergonomics. Proper hand placement and posture can prevent repetitive strain injuries, such as carpal tunnel syndrome.
Example
- Typing Speed: 80 WPM with 98% accuracy
- Extensive experience with 10-key numerical entry, CRM systems, and transcription
Software skills for resume
Software skills refer to the expertise in using various programs and tools to perform tasks efficiently. These skills are essential in many industries, particularly in fields such as technology, engineering, data analysis, design, and more.
Here's a general list of software skills you might consider including, categorized by type:
Productivity software
- Google Workspace (Docs, Sheets, Slides, Gmail, Drive)
- Apple iWork (Pages, Numbers, Keynote)
Project management tools
- Microsoft Project
- Asana
- Trello
- Basecamp
- Jira
Graphic design and multimedia software
- Adobe Creative Cloud (Photoshop, Illustrator, InDesign, Premiere Pro)
- Sketch
- Canva
- CorelDRAW
Programming and development
- Programming Languages (e.g., Python, Java, JavaScript, C++)
- Integrated Development Environments (e.g., Visual Studio Code, IntelliJ IDEA)
- Version Control (e.g., Git, SVN)
- Development Frameworks (e.g., React.js, Angular, Django, Flask)
Data analysis and visualization
- Microsoft Excel
- Tableau
- Power BI
- R
- Python Libraries (e.g., Pandas, NumPy, Matplotlib, Seaborn)
Database management
- SQL (Structured Query Language)
- MySQL
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Oracle
- PostgreSQL
Web development
- HTML/CSS
- JavaScript
- Content Management Systems (e.g., WordPress, Joomla)
- Web Development Frameworks (e.g., React.js, Angular, Vue.js)
Networking and system administration
- Linux/Unix Shell
- Windows Server
- Cisco IOS
- VMware
- Wireshark
Customer relationship management (CRM) software
- Salesforce
- HubSpot
- Zoho CRM
- Microsoft Dynamics
Statistical analysis software
- SPSS
- SAS
- Stata
- MATLAB
Hardware skills
Hardware skills encompass the knowledge, abilities, and expertise related to physical components of computers, electronic devices, and other systems.
While most people focus on their software skills, having strong hardware knowledge can also make you a valuable candidate. These computer skills are important for professionals working in IT support, computer engineering, electronics, telecommunications, and hardware development.
| Skill | Description |
|---|---|
| Computer assembly | Proficiency in assembling and disassembling computers, including installing and removing components like CPUs, RAM, hard drives, and expansion cards. |
| Troubleshooting | Ability to diagnose hardware issues and identify faulty components. |
| Peripheral installation and configuration | Experience in configuring peripherals such as printers, scanners, and external drives. |
| Networking equipment setup | Knowledge of setting up routers, switches, and other devices. |
| Hardware maintenance | Familiarity with routine tasks such as cleaning PC components. |
| Cable management | Skill in organizing and routing cables within a computer or networking setup. |
| Hardware testing and benchmarking | Experience in conducting tests to evaluate performance and stability. |
| Electronics repair | Proficiency in soldering components onto circuit boards and repairing electronic devices. |
| Server maintenance | Understanding of hardware components, including RAID configurations. |
| Data recovery | Knowledge of techniques and tools to retrieve data from damaged or corrupted storage devices. |
| Security hardware | Familiarity with biometric scanners, cameras, and access control systems. |
| Inventory management | Ability to track, document, and manage hardware assets to ensure proper availability and maintenance schedules. |
Operating systems knowledge
Operating systems (OS) is software that manage computer hardware resources and provide common services for different programs.
Include any operating systems you are proficient in on your resume, such as Windows, macOS, or Linux. You can also mention specific versions if applicable, like Windows 10 or macOS Catalina.
Example:
- Windows. Experienced user with proficiency in Windows 7, 8, and 10. Familiar with troubleshooting, system configuration, and software installation.
- Linux. Intermediate-level proficiency with Ubuntu and CentOS distributions. Comfortable with command-line interface (CLI), package management, and shell scripting.
- macOS. Competent user with MacOS X Yosemite and later versions. Proficient in system navigation, application installation, and troubleshooting.
- Mobile OS. Familiarity with iOS and Android operating systems. Proficient in device setup, app installation, and basic troubleshooting.
Having knowledge of multiple operating systems also demonstrates your versatility and adaptability in the workplace. Your adeptness in using a variety of tools and software is evident, making you an indispensable addition to any company.
Programming languages
With the rapid advancement of technology, proficiency in programming languages has become a highly valued computer skill among employers. This is particularly applicable for roles in the tech field or positions that entail working with data and analytics.
Your priority should be to showcase the languages that hold the greatest relevance to the job at hand. For example, if the position requires web development, be sure to list languages such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
Some other popular languages to consider adding to your resume include Python, Java, C++, and SQL. These languages have widespread usage across multiple industries and can highlight your adaptability as a candidate.
Remember to be honest about your level of proficiency in each language, as employers may test your skills during the interview process. Additionally, don't forget to include any certifications or projects that demonstrate your experience with these languages.
Ensure that you tailor the list of programming languages based on the requirements of the desired job and your actual proficiency level.
Database management skills
Database management involves organizing, storing, and retrieving data using specialized software. It is crucial for businesses to ensure their data is secure and easily accessible, making database administration expertise highly desirable.
When listing database management skills on your resume, ensure to mention specific software programs you are proficient in, such as SQL or Oracle.
- Additionally, mention any experience you have with data analysis or reporting, as this demonstrates your ability to extract useful information from large datasets.
Here are computer database skills examples for your resume:
Database platforms
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Oracle Database
Database design and modeling
- Experience in designing and implementing database schemas.
- Proficient in data modeling techniques such as ER diagrams and normalization.
Query optimization
- Skilled in writing complex SQL queries for efficient data retrieval.
- Experience in query optimization techniques to improve database performance.
Database administration
- Hands-on experience in database administration tasks such as backup and recovery, security management, and user access control.
- Understanding of database monitoring and maintenance tools.
Data warehousing
- Knowledge of data warehousing concepts and methodologies.
- Familiarity with designing and managing data warehouse solutions.
ETL processes
- Proficient in Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) processes for data integration.
- Experience with ETL tools like Informatica, Talend, or SSIS.
Database programming
- Proficiency in database programming languages like SQL, PL/SQL, T-SQL.
- Experience in developing stored procedures, triggers, and functions.
Data security and compliance
- Understanding of data security principles and compliance regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
- Experience in implementing data security measures such as encryption and access controls.
Troubleshooting and performance tuning
- Strong troubleshooting skills to identify and resolve database issues.
- Experience in performance tuning to optimize database performance.
Version control and documentation
- Proficient in version control systems like Git for managing database changes.
- Experience in documenting database designs, schemas, and processes.
Cloud database services
- Familiarity with web services such as Amazon RDS, Azure SQL Database, and Google Cloud SQL.
- Experience in deploying and managing databases in the cloud environment.
Database migration and upgrades
- Experience in database projects, including planning, execution, and post-migration validation.
- Proficient in upgrading database versions and applying patches.
Database manipulation skills can be especially beneficial in fields such as finance, marketing, and healthcare where data plays a vital role in decision-making processes.
Project management
Modern companies rely heavily on project management tools to streamline processes and ensure efficient operations. Demonstrating expertise in these digital programs can separate you from other job seekers and make you a valuable contributor to any organization.
A multitude of organizations utilize project management programs such as Asana, Trello, and Basecamp to keep track of tasks, deadlines, and team communication.
These tools necessitate basic computing abilities, but possessing advanced knowledge and experience with them can be a significant advantage for prospective employers.
Key project management software skills to highlight on your resume include:
- Familiarity with project planning and task delegation.
- Ability to create and maintain project schedules.
- Understanding of Agile and Scrum methodologies.
- Proficiency in utilizing Gantt charts and Kanban boards.
- Experience with task tracking and progress monitoring.
- Competence in collaborating with team members through the software.
- Knowledge of file sharing and document organization within the platform.
- Capability to generate detailed reports and analyze metrics for informed decision-making.
Incorporating these skills into your resume will reveal your mastery to effectively manage projects and collaborate with others. Ensure to include concrete instances of your utilization of these software programs in past roles or initiatives to demonstrate your proficiency.
Graphic design skills
If you're applying for a role in graphic, web, or UI/UX design, and any creative field, showcasing this type of computer skills is essential. Employers in these industries expect candidates to have a strong foundation in design principles and software proficiency.
However, even if you're not looking for a design-specific role, graphic skills can be valuable in many fields. Companies often need employees who can create visually appealing presentations, marketing collateral, reports, or even internal communications.
Your design skills make you more versatile and capable of fulfilling various tasks within the organization. Employers often prefer candidates who can handle other tasks in addition to their primary responsibilities.
Software skills:
- Proficient in Adobe Creative Suite (Photoshop, Illustrator, InDesign).
- Knowledgeable in other design software such as Sketch, Figma, or Canva.
- Familiarity with typography, layout, and color theory.
- Understanding of design best practices and principles.
- Ability to work with vector graphics and raster images.
- Experience with image editing, retouching, and manipulation.
- Proficiency in file formats for print and web (PDF, JPEG, PNG, SVG, etc.).
- Basic knowledge of HTML and CSS for web design.
Creative skills:
- Strong visual communication skills.
- Ability to conceptualize and develop creative ideas from concept to completion.
- Eye for detail and design aesthetics.
- Capacity to adapt design styles to different projects and clients.
- Experience in branding, logo design, and corporate identity development.
- Understanding of UX and UI design principles.
- Creativity in problem-solving and finding innovative design solutions.
- Ability to work collaboratively in a team environment and take constructive feedback.
Enterprise systems knowledge
Enterprise systems refer to large-scale software applications used by organizations to manage their business processes and data across various departments and functions.
These systems are typically integrated and centralized, providing a unified platform for managing core business functions such as finance, customer relationship, and human resources, supply chain management, etc.
In the modern job market, showcasing proficiency in enterprise systems can give you a competitive edge over other candidates. Employers often prioritize candidates who can quickly adapt to their existing systems and processes, reducing the time and resources required for training.
Here are examples of enterprise computer systems skills for a resume:
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- Proficient in implementing and managing ERP systems such as SAP, Oracle, and Microsoft Dynamics.
- Extensive experience with modules including Finance, Supply Chain Management, and Human Resources.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Skilled in configuring and customizing CRM platforms like Salesforce and Microsoft Dynamics CRM.
- Proven track record of optimizing sales processes and improving customer relationships through CRM implementation.
Business Intelligence (BI) and Analytics
- Strong understanding of BI tools such as Tableau, Power BI, and QlikView.
- Experience in data visualization, reporting, and dashboard creation to support decision-making processes.
Enterprise Content Management (ECM)
- Familiarity with ECM systems like SharePoint, Documentum, and OpenText.
- Proficient in designing document management solutions and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Supply Chain Management (SCM)
- Expertise in SCM platforms including SAP SCM, Oracle SCM Cloud, and JDA Software.
- Skilled in optimizing supply chain operations, demand planning, and inventory management.
In the current era of technology, being well-versed in enterprise systems is highly valued by employers in all sectors. So make sure to highlight this skill on your resume and stand out from the competition.
Social media
Familiarity and proficiency with diverse online networking channels are becoming increasingly crucial. Including these skills in one of your resume sections can highlight your expertise in digital communication.
Social media skills are highly relevant across various industries, including marketing, public relations, communications, advertising, journalism, e-commerce, and more.
Many companies recognize the importance of maintaining a strong presence on different social media platforms to engage with their audience, build brand awareness, and drive business results.
Here are some tips on how to present social media skills effectively on your resume:
- List specific platforms. Mention the platforms you're proficient in, such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn, TikTok, Snapchat, etc. Be sure to include platforms relevant to the job.
- Quantify your experience. If possible, mention the number of followers, engagement rates, or any specific achievements you've accomplished. For example, "Managed a Twitter account with over 10,000 followers and increased engagement by 30%".
- Analytics. If you have experience with tools like Facebook Insights, Twitter Analytics, or Google Analytics, mention your proficiency in analyzing data and using insights to optimize social media strategies.
- Use action verbs. When mentioning your skills and accomplishments, use strong action verbs. For example, instead of saying "Responsible for managing various media accounts", say "Managed social media accounts to increase engagement by 20%".
- Tailor to the job description. Customize your resume to match the description of the position you're applying for. If the job requires specific social media knowledge, highlight those skills.
- Content creation and curation. Showcase your capacity to produce and manage engaging posts, videos, and graphics tailored to different audiences and platforms.
Presence on social media can also demonstrate your ability to communicate and engage with others effectively. This is especially advantageous for positions that demand excellent communication and customer service.
Machine learning and artificial intelligence
These are two closely related fields that have gained significant attention in recent years due to their wide-ranging applications across various industries.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) is a broad concept that encompasses the development of systems or machines that can perform tasks that typically require humans. This includes visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation.
- Machine learning (ML) is a subset of AI that focuses on developing algorithms that enable computers to perform tasks without being explicitly programmed for them. In essence, it is about teaching machines to learn and improve over time.
The demand for professionals with expertise in this sphere is growing rapidly across industries such as healthcare, finance, retail, automotive, and more. Employers are actively seeking individuals who can develop AI-driven solutions to solve complex problems.
Here are some specific examples of AI computer skills to put on your resume:
Machine learning algorithms
- Supervised learning. Linear and Logistic Regression, Decision Trees, Random Forest, Support Vector Machines (SVM), Gradient Boosting Machines (GBM).
- Unsupervised learning. K-Means Clustering, Hierarchical Clustering, Principal Component Analysis (PCA), t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE).
- Deep learning. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN), Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN).
AI frameworks and libraries
- TensorFlow. An open-source machine learning framework by Google for building and training neural network models.
- PyTorch. A deep learning framework developed by Facebook's AI Research lab, known for its dynamic computational graph and ease of use.
- scikit-learn. A Python library that provides simple and efficient tools for data mining and analysis, including various ML algorithms.
By acquiring these skills now, you position yourself for career success in a rapidly evolving job market where automation and AI-driven technologies are becoming more prevalent.
Version control systems skills
Version Control Systems (VCS) are tools that help manage changes to source code or documents over time. They allow multiple people to work on a project simultaneously, keep a history of changes, and enable the restoration of previous versions if needed.
VCSs are critical for coordinating efforts and ensuring that everyone can work on the same project without conflicts. Below is how you can present your knowledge effectively.
Key tools to add:
- Git. Branching and merging, distributed workflows, large projects, and extensive community support.
- GitHub. Pull requests, issue tracking, GitHub Actions for CI/CD, wikis, and extensive community and integration ecosystem.
- GitLab. Built-in CI/CD pipelines, issue tracking, code review, wiki, and extensive integration capabilities.
- Bitbucket. Code collaboration, pull requests, pipelines for CI/CD, issue tracking, and integration with other Atlassian products like Jira.
- SVN (Subversion). Centralized repository model, atomic commits, versioned directories, and access control mechanisms.
- Mercurial. Branching and merging, decentralized architecture, extensibility through plugins, and simplicity of use.
VCS skills and competencies
Repository Management:
- Creating and managing repositories.
- Cloning, branching, and merging strategies.
- Handling large codebases and multiple repositories.
Branching Strategies:
- Git Flow.
- Feature branching.
- Trunk-based development.
Collaboration and Code Review:
- Pull (PRs) and merge requests (MRs).
- Code review practices and tools.
- Conflict resolution and merge conflict handling.
Commit Practices:
- Writing meaningful commit messages.
- Squashing commits.
- Reverting and cherry-picking commits.
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD):
- Setting up CI/CD using GitHub Actions, GitLab, and Bitbucket Pipelines.
- Automated testing and deployment.
Security and Compliance:
- Managing access controls and permissions.
- Ensuring code security through Version Control Systems tools.
- Compliance with version control policies and best practices.
Virtualization and cloud infrastructure management skills
| Skill | Description |
|---|---|
| Virtual Machine (VM) Management. | Creating, configuring, and maintaining machines using platforms like VMware, Hyper-V, or VirtualBox. |
| Hypervisor Proficiency. | Understanding technologies (e.g., VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, KVM) to manage virtualized environments. |
| Containerization. | Using containers to package applications and their dependencies, with tools like Docker and orchestration systems like Kubernetes. |
| Cloud Platform Management. | Managing cloud platforms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), or Oracle Cloud. |
| Cloud Security. | Ensuring the safety of environments, including configuring firewalls, encryption, IAM (Identity and Access Management), and compliance tools. |
| IaaS. | Understanding how to manage scalable virtualized resources such as compute, storage, and networking in cloud environments. |
| PaaS. | Utilizing platforms like AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Azure App Services, or Google App Engine to develop, manage, and deploy applications. |
| SaaS. | Managing and configuring applications like Salesforce, Office 365, or Google Workspace for business efficiency. |
| Cloud Automation Tools. | Using frameworks such as Terraform, Ansible, or AWS CloudFormation to automate infrastructure provisioning and management. |
| Load Balancing and Scaling. | Configuring balancers (e.g., AWS Elastic Load Balancer) and auto-scaling to ensure high availability and performance of applications. |
| Backup and Disaster Recovery. | Implementing strategies using tools like AWS Backup, Azure Site Recovery, or Veeam. |
| Cost Management and Optimization. | Monitoring and optimizing cloud infrastructure costs using tools like AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Cost Management, or Google Cloud’s Cost Calculator. |
| Network Virtualization. | Managing virtual networks (e.g., AWS VPC, Azure Virtual Network, GCP Virtual Private Cloud) and configuring VPNs or subnets. |
| Multi-Cloud Management. | Handling infrastructure across multiple cloud providers (AWS, Azure, GCP) and managing interoperability. |
| Storage Management. | Managing cloud storage solutions (e.g., AWS S3, Azure Blob, Google Cloud) and configuring scalable policies. |
| Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI). | Setting up and managing desktops for remote users using platforms like Citrix, VMware Horizon, or Microsoft Azure. |
| Monitoring and Performance Tuning. | Using tools like AWS CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, or Prometheus to optimize cloud resources. |
| High Availability (HA) Architectures. | Designing and deploying highly available systems using redundancy, failover, and cloud-native services to minimize downtime. |
| API Integration and Management. | Utilizing cloud APIs and services (e.g., AWS SDK, Azure APIs) for seamless integration between cloud platforms and third-party tools. |
Tips on describing computer skills for resume
How to accurately portray your proficiency levels without overwhelming the reader with technical jargon? Below are a few do's and don'ts to keep in mind when describing your skills on a resume.
Do's:
- Use clear terms. Use clear and widely understood terms to describe your proficiency level. For example, "Expert", "Proficient", "Intermediate", "Basic", or "Familiar".
- Be honest. Only claim proficiency levels that accurately reflect your skills. Misrepresenting can lead to difficulties in performing job responsibilities and can damage your credibility.
- Provide context. If possible, provide context or examples of how you've used your computer knowledge in previous roles or projects. This can help employers understand your level of proficiency better.
- Tailor to the job. Customize the description of your skills to match the requirements of the position. Highlight those that are most relevant to the job.
- Quantify when possible. If you have quantifiable achievements related to computer skills, such as increasing productivity or efficiency, include them on your resume. This will help demonstrate the value you can bring to potential employers.
Don'ts:
- Exaggerate. Avoid exaggerating your knowledge to make yourself appear more qualified than you actually are. Overstating your skills can lead to disappointment for both you and your employer if you're unable to meet expectations.
- Use vague terms. Avoid using non-specific terms that don't provide clear information about your proficiency, such as "Good" or "Excellent". These terms can mean different things to different people and may not accurately convey your skills.
- Forget to update. Make sure to regularly update your resume with any changes to your computer skills or proficiency levels. This ensures that your resume accurately reflects your current abilities and increases your chances of success in job applications.
Effectively depicting your computer literacy on a resume is vital for impressing potential employers. By adhering to these guidelines, you can successfully demonstrate your abilities and improve the prospects of securing the position.
Create your professional Resume in 10 minutes for FREE
Build My Resume
Conclusion
Ultimately, showcasing both advanced and basic computer skills on your job resume can greatly improve the chances of obtaining the desired job. By following the tips and examples provided in this article, you can effectively showcase your proficiency in various programs and tools.
Continue to develop and improve your computer skills as technology is constantly evolving in the workplace. Keep your resume updated with any new skills you acquire, and don't be afraid to highlight them during interviews or in cover letters.
FAQ
- What if I don't have any specific technical skills?
- Even if you have no experience with particular software or systems, highlighting your overall comfort and understanding of technology can still be beneficial. Additionally, consider taking courses or online tutorials to build your technical skillset.
- Do I need to list fundamental computer competencies?
- It's generally not necessary to include very basic skills such as using email or word processing. However, if the job description specifically mentions these skills, it may be worth mentioning them. This way you will show that you meet all of the required qualifications.
- Should I mention proficiency levels (e.g., beginner, intermediate, advanced) for each computer skill?
- It's optional but can be helpful, especially for technical roles, to provide an indication of your proficiency level.
- How do I showcase my computer skills for resume if I'm transitioning to a new career?
- Emphasize transferable skills and highlight any relevant experience, projects, or training that show your ability to adapt to new technologies.
- How can I show that I’m a fast learner with computer skills?
- Mention any instances where you quickly adapted to new software or technologies, and highlight any self-learning or courses you've taken.
- Can I include mobile app skills on my resume?
- Yes, if you have experience with specific software that relate to your field, such as productivity apps, graphic design tools, or industry-specific programs, it can be valuable to list them.